
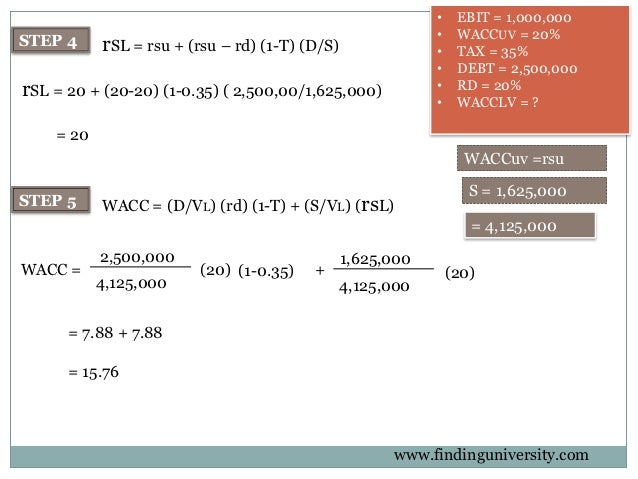
So, as the number of water vapor molecules increases in the air above the water, the condensation rate increases, too. As the number of water vapor molecules increases, the chance of a water vapor molecule contacting the interface between air and water and condensing back into liquid also increases, which translates to an increase in the condensation rate. But, as time goes on, and net evaporation continues, the air above the water contains an increasing number of water vapor molecules. In fact, the evaporation rate far exceeds the condensation rate early on (net evaporation occurs). Initially, the condensation rate is small because only few water vapor molecules are present, and the probability that any one of them will come in contact with the interface between air and water is low. As time passes and as and more water molecules enter the vapor phase in the space above the water, some water vapor molecules condense back into liquid as they come in contact (by chance) with the interface between the liquid water and the air above. In time, the most energetic water molecules break the molecular bonds with their neighbors and evaporate into the space above the water, gradually increasing the number of water vapor molecules there. Now, let's pour some water into the container and see what happens. What about the condensation rate? To explore the controllers of the condensation rate, let's perform a little experiment, starting with a closed, empty container filled with dry air (no water vapor molecules). Lower water temperatures yield lower evaporation rates, while higher water temperature yield higher evaporation rates. So, that means water temperature is a major controller of the evaporation rate.

Of course, as you know, the vibration of molecules depends on temperature: the higher the temperature, the faster the molecular vibrations, and the more likely a liquid water molecule will break free from its neighbors and evaporate into water vapor.

To better understand how net evaporation and net condensation are achieved, we need to understand a bit more about what controls the evaporation rate (the number of water molecules evaporating in a given area over a given time period) and the condensation rate (the number of water vapor molecules condensing into liquid water in a given area over a given time period).įor starters, the bonds that loosely connect water molecules in the liquid phase aren't all that strong, so occasionally, the natural vibration of water molecules breaks these bonds, resulting in evaporation. The states of net evaporation and net condensation are extremely important to weather forecasters, because they have implications for cloud and precipitation formation, as well as evaporation of precipitation (and subsequent evaporational cooling) among other things. On the other hand, assuming you have some liquid water present to begin with, "net" evaporation, which means that the evaporation rate exceeds the condensation rate, causes liquid water droplets to shrink (or disappear altogether), or puddles on the ground to dry up, etc. "Net" condensation means that the condensation rate exceeds the evaporation rate causing liquid water droplets to form. Obvious phase changes occur when there's either "net" condensation or "net" evaporation (assuming you have some liquid water to begin with). In the last section, I asserted something that may have been surprising: evaporation and condensation are occurring around you simultaneously all the time, but you often don't see the results because they're happening on the molecular level.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
